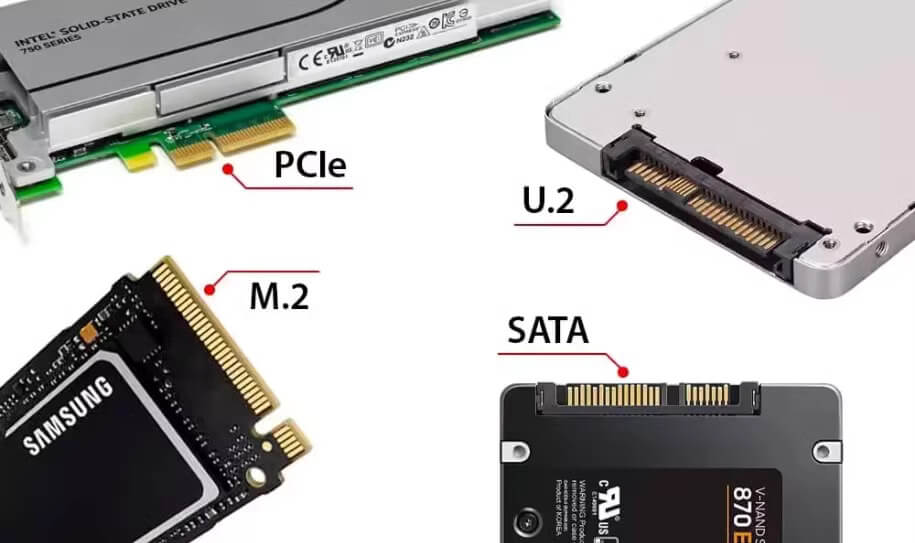
The U.2 interface is a physical specification for connecting storage devices, such as Solid-State Drives (SSDs), to a computer’s motherboard. Formerly known as SFF-8639, U.2 is most modern discovery with a high-speed interface that utilizes a PCIe lane to connect storage devices, enabling faster data transfer rates than traditional SATA III interfaces.
Advantages of U.2 SSDs
U.2 SSDs offer several advantages over traditional storage devices. One of the most significant benefits is higher bandwidth. U.2 supports up to 4 lanes of PCIe 3.0, resulting in a maximum bandwidth of 32 Gb/s. This means that U.2 SSDs can transfer data at incredibly fast speeds, making them ideal for applications that require high-performance storage.
Another advantage of U.2 SSDs is their hot-swappable design. This feature allows users to replace or upgrade storage devices without shutting down the system, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. Additionally, U.2 SSDs are more compact than traditional 2.5-inch SSDs, making them perfect for compact systems where space is limited.
Drawbacks of U.2 SSDs
Despite their many advantages, U.2 SSDs also have some drawbacks. One of the main limitations is limited adoption. U.2 is not as widely adopted as other interfaces, such as M.2 or SATA, which can make it difficult to find compatible systems or accessories. Additionally, U.2 SSDs may not be compatible with older systems, which can make upgrading more challenging.
NVMe Protocol: Optimized for Flash Storage
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a protocol designed specifically for flash storage, such as SSDs. It’s a high-speed, low-latency protocol that enables storage devices to communicate with the system more efficiently. NVMe supports up to 64 Gb/s of bandwidth, making it significantly faster than traditional SATA III interfaces.
One of the key benefits of NVMe is its low latency. NVMe has lower latency than traditional storage protocols, resulting in faster access times and improved system performance. Additionally, NVMe allows for parallel processing of multiple commands, further increasing performance and efficiency.
Influence of U.2 and NVMe on PC Performance
The combination of U.2 and NVMe has a significant impact on PC performance. With U.2 providing a high-speed interface and NVMe enabling efficient communication, storage devices can access data at incredibly fast speeds. This results in improved system performance, faster boot times, and faster application loading.
Faster storage access also increases productivity, as users can work more efficiently and complete tasks faster. Moreover, the enhanced performance provided by U.2 and NVMe can improve the gaming experience, reducing loading times and improving overall gameplay.
| NAME | SPECS | RATING | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Micron 9300 Pro 3.84TB N VMe U.2 Enterprise Solid State Drive |
|
9.5 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
||
|
9.7 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
8.7 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
9.3 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
9.8 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
8.7 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
9.6 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
8.3 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
8.6 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
|||
|
9.5 5/5 Stars WiseScore ? |
HDD vs. SSD: Comparing Storage Technologies
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are two common types of storage devices. HDDs use spinning disks and mechanical heads to store data, resulting in slower access times and lower performance. SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory to store data, providing faster access times and higher performance.
SSDs are a type of storage device that uses flash memory to store data. U.2 and NVMe are technologies that enable faster communication between the storage device and the system. Combining SSDs with U.2 and NVMe results in even faster storage access and improved system performance.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the technologies used in NVMe U.2 SSDs:
NAND
- NAND (Not And) flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage that retains data even when power is turned off.
- In NVMe U.2 SSDs, NAND flash memory is used to store data.
- There are different types of NAND flash memory, including:
- SLC (Single-Level Cell): Stores one bit per cell, offering high performance and endurance, but higher cost.
- MLC (Multi-Level Cell): Stores two bits per cell, offering a balance between performance, capacity, and cost.
- TLC (Tri-Level Cell): Stores three bits per cell, offering high capacity at a lower cost, but with lower performance and endurance.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell): Stores four bits per cell, offering even higher capacity at a lower cost, but with lower performance and endurance.
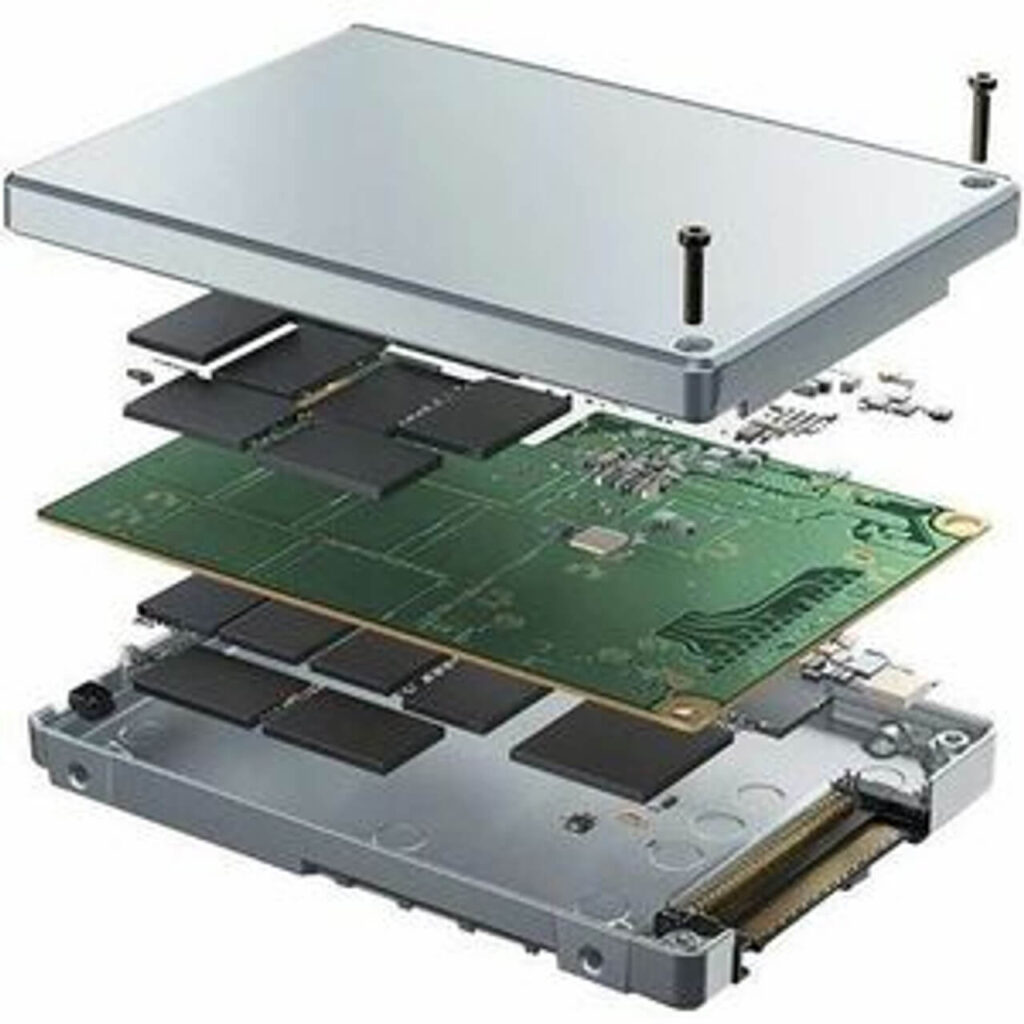

Static and Dynamic Wear Levelling
- Wear levelling is a technique used to evenly distribute write operations across the entire SSD, ensuring that no single block or page wears out faster than others.
- Static wear levelling is a technique that pre-maps the SSD’s blocks and pages to ensure even wear levelling from the start.
- Dynamic wear levelling is a technique that continuously monitors and adjusts the wear levelling process in real-time, taking into account the SSD’s usage patterns.
Power Loss Protection (Power Caps)
- Power loss protection is a feature that protects data in the event of a sudden power loss.
- Power caps are small capacitors that store energy and allow the SSD to complete any pending write operations in the event of a power loss.
- This ensures that data is not lost or corrupted due to power failure.
Enterprise SMART Tools
- SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) is a set of tools that monitor the SSD’s health and performance.
- Enterprise SMART tools provide advanced monitoring and reporting capabilities, including:
- Real-time monitoring of SSD health and performance
- Predictive failure analysis
- Performance optimization
- Error correction and detection
Reliability Tracking, Usage Statistics, SSD Life Remaining, Wear Levelling, Temperature
- Reliability tracking: The SSD monitors its own reliability and reports any issues or errors.
- Usage statistics: The SSD tracks usage patterns, including read and write operations, to optimize performance and endurance.
- SSD life remaining: The SSD estimates its remaining lifespan based on usage patterns and wear levelling.
- Wear levelling: The SSD continuously monitors and adjusts wear levelling to ensure even wear across the entire device.
- Temperature: The SSD monitors its operating temperature and adjusts performance accordingly to prevent overheating.
Endurance
- Endurance refers to the SSD’s ability to withstand a certain number of write cycles before wearing out.
- NVMe U.2 SSDs are designed to provide high endurance, with some models offering up to 3,000 TBW (Terabytes Written) or more.
Power Consumption
- Power consumption refers to the amount of power required to operate the SSD.
- NVMe U.2 SSDs are designed to be power-efficient, with some models consuming as little as 2-3 watts.
Storage Consumption
- Storage consumption refers to the amount of storage capacity used on the SSD.
- NVMe U.2 SSDs are available in a range of capacities, from 100 GB to 16 TB or more.
Storage Temperature
- Storage temperature refers to the recommended temperature range for storing the SSD when not in use.
- NVMe U.2 SSDs typically have a storage temperature range of -40°C to 85°C.
Operating Temperature
- Operating temperature refers to the recommended temperature range for using the SSD.
- NVMe U.2 SSDs typically have an operating temperature range of 0°C to 70°C.
What is the key Difference between M.2 SSD and U.2 SSD?
M.2 and U.2 are both interfaces used for connecting solid-state drives (SSDs) to a computer’s motherboard. While they share some similarities, there are key differences between the two:
M.2 SSD:
- Physical Interface: M.2 is a smaller, compact connector (22mm wide, 42mm to 110mm long) that uses a keying system to ensure correct installation.
- Protocols: M.2 supports multiple protocols, including SATA, PCIe, and NVMe.
- Speed: M.2 SSDs can operate at various speeds, including SATA (up to 600 MB/s), PCIe x2 (up to 16 GB/s), and PCIe x4 (up to 32 GB/s).
- Power: M.2 SSDs typically draw power from the motherboard, with a maximum power consumption of 3.3V or 5V.
- Compatibility: M.2 is widely supported by modern motherboards, laptops, and desktops.
U.2 SSD:
- Physical Interface: U.2 is a larger, rectangular connector (15mm wide, 25mm long) that uses a latch to secure the drive.
- Protocols: U.2 primarily supports PCIe and NVMe protocols.
- Speed: U.2 SSDs can operate at higher speeds, up to PCIe x4 (up to 32 GB/s) or even PCIe x8 (up to 64 GB/s) in some cases.
- Power: U.2 SSDs can draw more power than M.2 SSDs, with a maximum power consumption of 12V or 15V.
- Compatibility: U.2 is less widely supported than M.2, but is still found in some high-end motherboards, workstations, and servers.
Key differences:
- Size and form factor: M.2 is smaller and more compact, while U.2 is larger and more rectangular.
- Protocol support: M.2 supports SATA, PCIe, and NVMe, while U.2 primarily supports PCIe and NVMe.
- Speed: U.2 can support faster speeds, especially with PCIe x8 connectivity.
- Power consumption: U.2 SSDs can draw more power than M.2 SSDs.
- Compatibility: M.2 is more widely supported than U.2, but U.2 is still used in high-end systems.
In summary, M.2 is a more versatile and widely supported interface, suitable for mainstream applications, while U.2 is a higher-performance interface, better suited for high-end systems that require faster storage and more power.

In which case I should choice U.2 SSD for my Personal Computer
You should choose a U.2 SSD for your personal computer if you need the highest possible performance and have a motherboard that supports it. Here’s a breakdown of when a U.2 SSD is a good choice and when it might not be:
Reasons to Choose a U.2 SSD:
- Exceptional Speed: U.2 SSDs, especially those using the NVMe protocol, offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to SATA or even some M.2 NVMe drives. This translates to quicker boot times, faster application loading, and improved overall system responsiveness, particularly beneficial for demanding tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and gaming. They can achieve speeds up to 15,800 MB/s.
- High Bandwidth: U.2 interfaces utilize multiple PCIe lanes (typically four), providing a much higher bandwidth than SATA. This allows for sustained high-speed data transfer, crucial for applications that handle large files.
- Hot-Swappable: U.2 drives are often hot-swappable, meaning you can remove or replace them without powering down your system. This is a significant advantage for servers and high-availability systems but less critical for typical desktop PCs.
- Large Capacity: U.2 SSDs are available in high capacities, suitable for users with extensive storage needs.
Reasons NOT to Choose a U.2 SSD:
- Motherboard Compatibility: Not all motherboards have U.2 connectors. You’ll need to check your motherboard specifications to ensure compatibility. If your motherboard doesn’t have a U.2 port, you’ll need an adapter card, which can add complexity and potentially reduce performance.
- Cost: U.2 SSDs are generally more expensive than comparable M.2 NVMe SSDs.
- Size and Physical Installation: U.2 drives use a 2.5-inch form factor, requiring a dedicated drive bay. This may be less convenient than the smaller M.2 form factor, which slots directly onto the motherboard.
- Overkill for Typical Use: For most everyday computing tasks, a high-speed M.2 NVMe SSD will likely provide sufficient performance without the added cost and compatibility considerations of a U.2 drive.
In summary:
A U.2 SSD is a top-tier choice for high-performance computing needs in systems with appropriate motherboard support. However, for average users, the performance gains might not justify the higher cost and potential installation complexities compared to M.2 NVMe SSDs. Carefully consider your specific needs and system capabilities before making a decision.
















[…] noted, as the Samsung 990 Pro M.2 NVMe SSD 2TB is a highly rated and popular choice among users and critics […]