Understanding sRGB in Computer Monitors
Introduction
Hey there! Today, we’re diving into the world of computer monitors and a term you’ll often hear: sRGB. This color space is key to displaying images and videos accurately on your screen. We’ll explore what sRGB is, how it works with your computer’s hardware, why it’s important, and how to use it effectively. Let’s make it simple and fun, like a friendly chat, to help you get the most out of your monitor.

What is sRGB?
sRGB stands for Standard Red Green Blue. It’s a color space, which means it’s a specific range of colors that your monitor can display. Think of it like a box of crayons with a unique set of colors. These colors are used to make sure everything you see on your screen looks right, no matter what device you’re using.
Why is sRGB Important?
sRGB is essential because it ensures consistency and accuracy in the colors you see across different devices. Here are some reasons why sRGB is important:
- Consistency: Colors look the same whether you’re viewing them on a computer, phone, or TV.
- Accurate Colors: sRGB helps your monitor show colors as they are meant to be seen.
- Standardization: Most devices and software use sRGB, making it a common language for colors.
How Does sRGB Work?
sRGB works by defining a specific range of colors that monitors should display. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Color Space: Think of sRGB as a box of crayons with specific colors inside. This set of colors is used to ensure everything looks correct on your screen.
- Calibration: Monitors use sRGB to adjust their colors. Calibration ensures that the colors you see are true to life, like tuning a musical instrument to make sure it sounds just right.
- Standard Colors: sRGB defines standard colors used everywhere, from websites to video games, ensuring that a blue sky in a game looks the same on every monitor.

The Role of Computer Hardware
Your computer is made up of different parts that all work together to show you those pretty pictures and videos. Let’s break it down:
- Monitor: This is your computer screen where you see everything. When you’re using sRGB, your monitor is like a canvas that shows all the colors in the sRGB crayon box.
- Graphics Card (GPU): This is like the artist who paints the picture. The GPU takes the colors from the sRGB crayon box and puts them on your monitor. It processes the images and makes sure they look right.
- Processor (CPU): Think of the CPU as the brain of your computer. It tells the GPU what to do. When you open a photo or video, the CPU says, “Hey GPU, use these sRGB colors to show this picture on the monitor!”
- Memory (RAM): This is like a sketchpad where temporary information is stored while the picture is being painted. It helps the CPU and GPU work faster.
- Storage (Hard Drive or SSD): This is where all your photos, videos, and other files are saved. When you open a file, the CPU and GPU fetch it from the storage and use the sRGB colors to display it on your monitor.
Understanding Monitor Color Gamut and the Role of sRGB
For those well-versed in monitor technology, delving into how a monitor’s color gamut functions, particularly in the context of sRGB, offers a deeper understanding of color accuracy and display performance. Let’s explore the technical aspects of color gamut and sRGB, and how they interplay to influence display quality.
Color Gamut: A Technical Overview
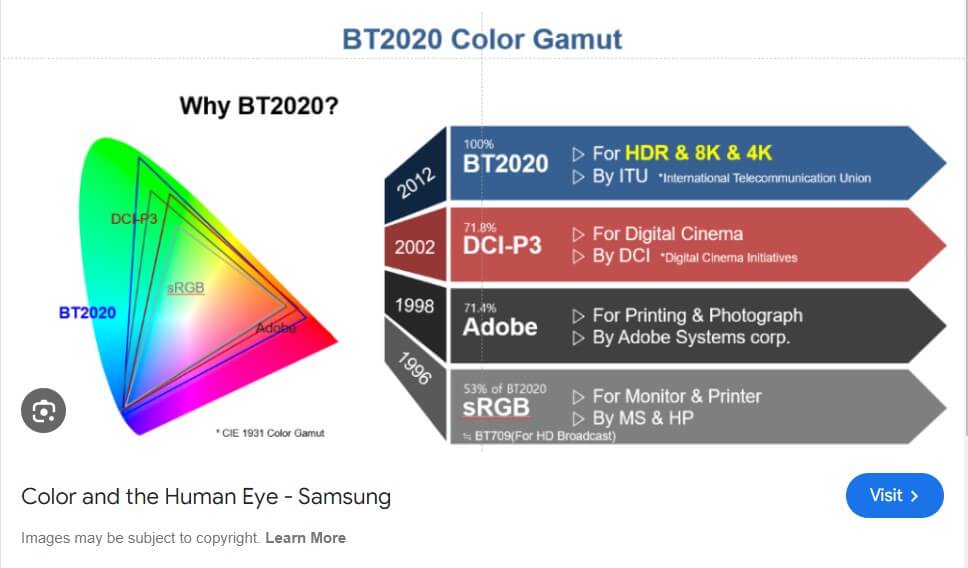
Color gamut refers to the range of colors that a monitor can reproduce. This range is typically represented as a subset of a larger color space, such as CIE 1931 XYZ color space, which encompasses the full spectrum of visible colors. The color gamut defines the extent of colors that can be displayed and is often visualized as a 2D or 3D shape within the color space.
Key Components Include:
- Primaries: The fundamental colors used by the monitor, which can be combined to create other colors. These are usually red, green, and blue (RGB) for monitors.
- Color Space Boundaries: The limits of the color gamut are defined by the spectral characteristics of the display’s phosphors or LEDs. These boundaries form a triangle or polygon within the 1931 CIE XYZ color space, indicating the achievable range of colors.
sRGB: The Standard Color Space
sRGB (Standard Red Green Blue) is a specific color space created by HP and Microsoft in 1996. It defines a standardized range of colors and is widely used in digital imaging and displays due to its broad compatibility and ease of use.
Key aspects include:
- Color Primaries: sRGB uses standard RGB primaries with specific chromaticities defined in the CIE 1931 color space. The primaries are designed to match the characteristics of typical consumer monitors and printers.
- Gamma Curve: sRGB employs a gamma curve of approximately 2.2, which models the non-linear relationship between input values and displayed brightness. This gamma correction ensures that images appear consistent with human visual perception.
The Role of sRGB in Monitor Color Gamut
1. Color Gamut Coverage: Monitors that support sRGB are designed to cover the sRGB color gamut fully or partially. This means that the monitor’s RGB primaries and their combinations are aligned with the sRGB standard, allowing it to accurately reproduce colors within this gamut. For instance:
- Full sRGB Coverage: A monitor with full sRGB coverage can reproduce the entire range of colors defined by the sRGB color space. This is ideal for applications where color consistency and accuracy are critical, such as web design or general consumer use.
- Partial sRGB Coverage: Monitors with partial coverage might reproduce a subset of sRGB colors. While they can still display sRGB content, the color fidelity may be compromised, especially in highly saturated or specific hues.
2. Calibration and Profile Management: Effective color management involves calibrating the monitor to ensure that it accurately adheres to the sRGB color space. This process includes:
- Factory Calibration: Many monitors come pre-calibrated to match sRGB standards. However, regular recalibration is necessary to maintain accuracy over time.
- ICC Profiles: Monitors use ICC (International Color Consortium) profiles to manage color reproduction. These profiles map the monitor’s color gamut to sRGB, ensuring that colors are rendered accurately in software that supports color management.
3. Practical Implications: The role of sRGB in the monitor’s color gamut has practical implications for various use cases:
- Web and Digital Media: sRGB is the default color space for web content and digital media. Monitors with accurate sRGB coverage ensure that content appears as intended across different devices.
- Print and Professional Work: While sRGB is sufficient for general use, professional applications such as high-quality printing often require wider gamuts like Adobe RGB or DCI-P3. Monitors with broader gamuts can better handle color-critical tasks, although sRGB remains a benchmark for consistency.
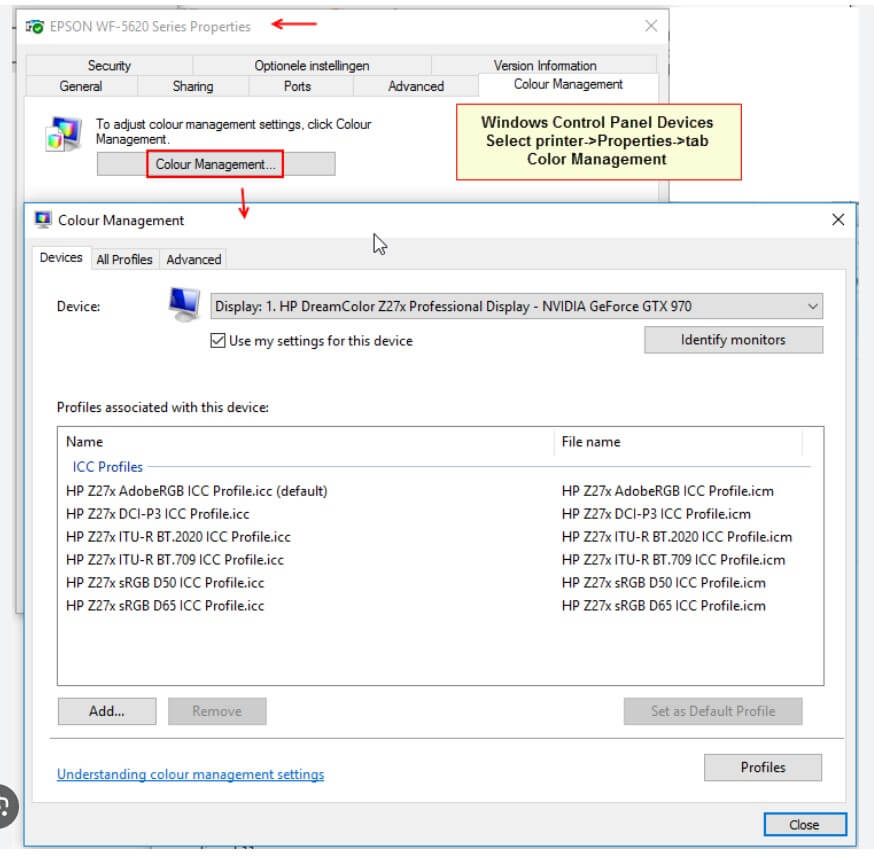
How to Switch to sRGB Mode on a Windows Computer
Switching to sRGB mode on a Windows computer is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Open Windows Settings: Click on the Start menu and select the gear icon to open Settings.
- Go to System and Choose Display: In the System settings, click on Display.
- Look for Color Profile and Choose sRGB: Under the Display settings, look for the Color Profile section and choose sRGB from the drop-down menu.
How to Switch to sRGB Mode on a Mac
Switching to sRGB mode on a Mac is also simple. Here’s how:
- Click on the Apple Icon and Choose System Settings: Click the Apple icon in the top-left corner and select System Settings from the menu.
- Click on Displays: In the System Settings, click on Displays.
- Open the Color Menu and Choose the sRGB Color Gamut: In the Displays settings, open the Color menu and choose the sRGB color gamut installed with your operating system. It will have an extension indicating the version you have.
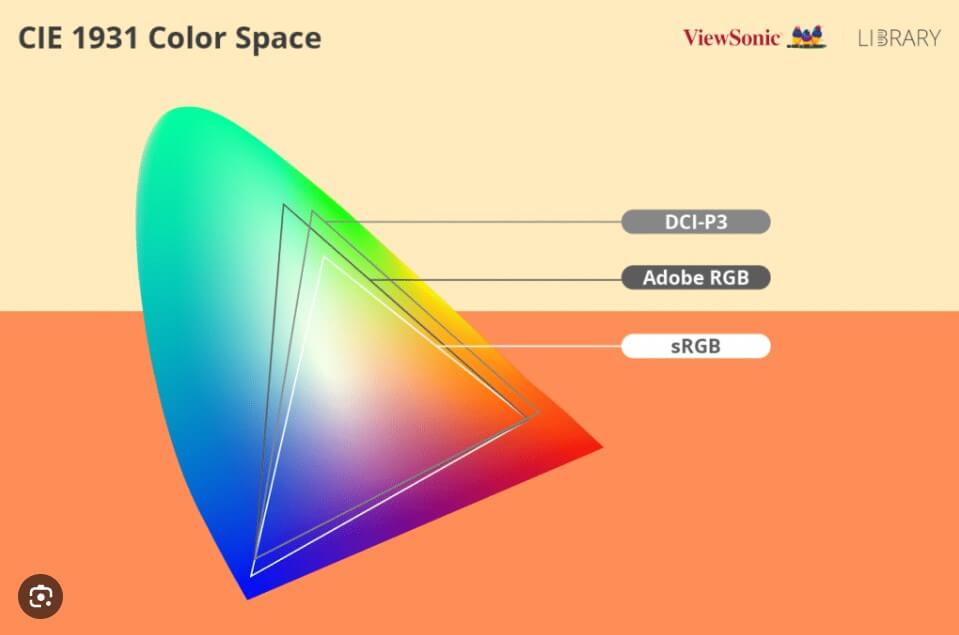
sRGB vs. Adobe RGB
Adobe RGB is another popular color space, especially in professional photography and graphic design. Here’s a quick comparison:
- Color Range: Adobe RGB has a wider color range than sRGB, making it better for high-end photo editing and printing.
- Complexity: Adobe RGB is more complex to work with, which might not be ideal for beginners.
- Compatibility: Not all devices and platforms support Adobe RGB, so your work might not look the
- same everywhere.
sRGB vs. DCI-P3
DCI-P3 is a color space commonly used in digital cinema and high-end monitors. Here’s how it compares to sRGB:
- Color Range: DCI-P3 covers a wider color gamut than sRGB, offering more vibrant and diverse colors.
- Usage: DCI-P3 is often used in 4K TVs, digital cinema, and some high-end monitors.
- Compatibility: Like Adobe RGB, not all devices support DCI-P3, which can lead to inconsistencies.
sRGB in Different Devices
sRGB is used in various types of monitors to ensure color accuracy. Here are a few examples:
- Office Monitors: Most office monitors use sRGB to display documents, websites, and videos accurately. This makes sure that everything looks consistent.
- Gaming Monitors: Many gaming monitors support sRGB to provide vibrant and realistic colors in games. This makes the gaming experience more immersive.
- Professional Monitors: Monitors used by designers and photographers often have a wider color range but still support sRGB for standard tasks. This ensures their work looks good on all devices.
sRGB in Image Editing and Post-Processing
For photo editing and post-processing, using sRGB ensures that the colors you see on your screen will match those on other sRGB-compliant devices. This is especially important for sharing your work online or printing it.
Limitations of sRGB Mode
While sRGB is great for many purposes, it does have its limitations:
- Narrower Color Range: sRGB covers a smaller portion of the visible color spectrum compared to other color spaces like Adobe RGB and DCI-P3.
- Less Vibrant Colors: Because of its narrower range, sRGB may not display as many vibrant colors as other color spaces.
Limitations and Solutions of sRGB
While sRGB has its limitations, there are ways to work around them:
- Calibration: Calibrating your monitor can help you achieve more accurate colors, even within the sRGB space.
- Software: Using photo editing software that supports color management can help you work within sRGB more effectively.
Final Words on sRGB Color Space
sRGB is a reliable and widely-used color space that ensures consistency and compatibility across various devices and platforms. While it has some limitations, its simplicity and broad usage make it an excellent choice for most users. Whether you’re editing photos, designing graphics, or just want accurate colors on your screen, sRGB is a solid option.
By understanding sRGB and how to use it, you can achieve more consistent and accurate colors in your work, making it look its best no matter where it’s viewed.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Can I Use sRGB Mode for Printing?
Yes, you can use sRGB mode for printing, but keep in mind that sRGB is not the best choice for all types of printing. While it’s fine for most consumer-grade prints, professional printers might use wider color spaces like Adobe RGB. If you’re printing high-end photos or artwork, you might need to convert your files to a different color space before printing.
What if My Monitor Doesn’t Support sRGB Mode?
If your monitor doesn’t support sRGB mode, you can still get close to accurate colors by calibrating your monitor. Calibration tools like colorimeters can help you adjust your display settings to match the sRGB color space as closely as possible.












2 Responses